Understanding the Components of Satellite Communication
Satellite communication systems consist of multiple components that work together to transmit signals across vast distances. These components are divided into three main segments: the space segment, the ground segment, and the user segment. Each segment has a unique function that ensures effective communication for various applications, including television broadcasting, internet connectivity, and global positioning systems (GPS).
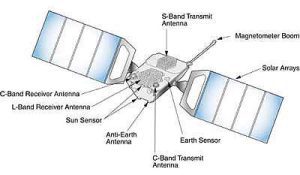
1. Space Segment: The Satellite System
The space segment includes the satellites that relay communication signals between different points on Earth.
a. Communication Satellites
Communication satellites operate in different orbits, including geostationary orbit (GEO), medium Earth orbit (MEO), and low Earth orbit (LEO). They carry transponders, which receive signals, amplify them, and transmit them back to the Earth.
b. Transponders
A transponder is a crucial component that consists of a receiver, amplifier, and transmitter. It processes incoming signals and sends them back with increased strength to ensure efficient transmission.
c. Antennas and Solar Panels
Satellites are equipped with antennas to receive and transmit signals. They also rely on solar panels to generate power for their operations, ensuring continuous communication services.
2. Ground Segment: Earth Stations and Control Centers
The ground segment consists of infrastructure on Earth that manages and controls satellite operations.
a. Earth Stations
Earth stations serve as the interface between satellites and user devices. They transmit and receive signals from satellites and connect them to communication networks.
b. Telemetry, Tracking, and Command (TT&C) Systems
TT&C systems monitor satellite performance, track their position in orbit, and send control commands to adjust their operations when necessary.
c. Network Control Centers
Network control centers manage the flow of data, ensuring signals are transmitted accurately and efficiently across communication networks.
3. User Segment: Receivers and Transmitters
The user segment includes devices that receive and transmit signals from satellites, allowing end-users to access communication services.
a. Satellite Phones and Internet Terminals
Satellite phones and terminals enable users in remote locations to access communication services, bypassing terrestrial networks.
b. Television and Radio Broadcast Receivers
Satellite TV and radio receivers pick up signals from satellites to provide uninterrupted broadcasting services.
c. GPS Devices
GPS devices rely on signals from navigation satellites to provide accurate positioning and navigation services worldwide.
Advancements in Satellite Communication Technologies
1. High-Throughput Satellites (HTS)
HTS technology improves bandwidth efficiency, allowing more data to be transmitted at higher speeds, making satellite internet more competitive with fiber-optic networks.
2. Software-Defined Satellites (SDS)
SDS technology enables real-time reconfiguration of satellite functions, improving adaptability and performance for different applications.
3. Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Satellite Networks
Companies like SpaceX and OneWeb are deploying LEO satellite constellations to provide global high-speed internet with reduced latency compared to GEO satellites.
The Future of Satellite Communication
As demand for global connectivity grows, satellite communication will continue to evolve with advanced technologies, increased efficiency, and expanded coverage. Whether for broadband internet, disaster response, or navigation, satellite communication remains a critical part of modern infrastructure.
For more insights into satellite communication technologies, explore our detailed guide on satellite platform components.
