Introduction to Reaction Wheel System in Spacecraft
The reaction wheel system (RWS) is a fundamental technology in spacecraft attitude control. It allows precise orientation changes of satellites or space probes, crucial for tasks like capturing images, maintaining communication, and conducting experiments in space. This technology has become indispensable for space agencies and private aerospace companies due to its efficiency and reliability.
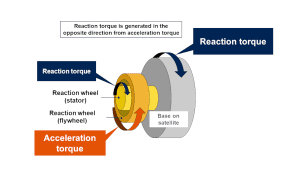
How Does the Reaction Wheel System Work?
The reaction wheel system operates based on the principles of angular momentum. It consists of several wheels mounted on the spacecraft’s axis of rotation. These wheels spin at varying speeds, generating counteracting forces that change the spacecraft’s orientation without the need for fuel-consuming thrusters.
1. Angular Momentum Transfer
When a reaction wheel accelerates or decelerates, it transfers angular momentum to the spacecraft, causing it to rotate in the opposite direction. By adjusting the speed of the wheels, the spacecraft can achieve precise attitude control and maintain its orientation relative to a reference point, such as Earth or a celestial body.
2. Efficiency and Precision
Unlike other systems that rely on fuel or physical thrusters, reaction wheels offer an energy-efficient solution with high precision. They are capable of fine-tuning the spacecraft’s attitude with minimal energy consumption, making them ideal for long-duration space missions.
Key Applications of Reaction Wheel Systems
1. Satellite Attitude Control
One of the most common uses of reaction wheels is in satellite attitude control. Satellites need to maintain specific orientations for tasks such as imaging, communications, and scientific data collection. Reaction wheel systems provide the necessary precision to keep satellites oriented correctly without consuming fuel.
2. Space Probe Navigation
Space probes and rovers also benefit from reaction wheels, especially in deep-space missions. These systems enable spacecraft to adjust their orientation for scientific observations or to align antennas for communication with Earth.
3. Space Telescope Stabilization
Space telescopes, such as the Hubble Space Telescope, rely on reaction wheels to maintain their orientation in space. These telescopes need to stay perfectly still for long exposure times when capturing detailed images of distant celestial bodies.
Benefits of Using a Reaction Wheel System
1. Fuel-Free Operation
One of the key advantages of the reaction wheel system is that it does not require fuel or propellant to change orientation. This makes it ideal for missions where fuel efficiency is critical, allowing spacecraft to operate for extended periods without worrying about fuel depletion.
2. High Precision and Reliability
Reaction wheel systems offer high precision in attitude control, which is essential for tasks like Earth observation, scientific data collection, and navigation. The technology has proven to be reliable in various space missions, ensuring spacecraft can operate effectively in the harsh environment of space.
3. Compact and Lightweight Design
The compact design of reaction wheels makes them suitable for space applications where weight and space are limited. These systems are lightweight, contributing to the overall efficiency of the spacecraft, which is crucial for long-duration missions.
Challenges and Limitations of Reaction Wheel Systems
1. Wheel Saturation
One limitation of reaction wheels is that they can become “saturated” after prolonged use. This occurs when the wheels can no longer generate enough torque to adjust the spacecraft’s orientation. In such cases, the reaction wheels need to be de-saturated by using other methods, such as magnetic torquers or control moment gyroscopes.
2. Wear and Tear
Over time, reaction wheels can experience wear and tear, which may impact their performance. While they are generally reliable, engineers must consider factors like motor degradation and mechanical stress when designing these systems.
3. Limited Torque Generation
While reaction wheels are excellent for fine-tuning spacecraft orientation, they have limitations in terms of the amount of torque they can generate. For larger spacecraft or those requiring significant attitude changes, additional systems may be needed in conjunction with reaction wheels.
The Future of Reaction Wheel Technology
As space exploration continues to advance, reaction wheel technology is also evolving. With improved materials, more efficient motors, and better integration with other control systems, reaction wheels are expected to become even more reliable and effective. In the future, reaction wheel systems could play a crucial role in more complex missions, such as interplanetary travel and deep space exploration.
